For some persistent skin conditions, topical treatments may not achieve the desired results.
While light therapy has existed for over a century (initially for chronic pain, joint and soft tissue injuries), its use for the treatment of skincare conditions is relatively recent.
In addition to treating mood and sleep disorders, as well as some forms of cancer and pre-cancer, the restorative properties of light therapy have also been adapted for cosmetic use. This makes it a less abrasive alternative to other skincare treatments like chemical peels.
Intense Pulse Light (IPL)
Otherwise known as phototherapy, light therapy uses waves of light to address various skin conditions, such as IPL for pigmentation. Also known as a “photofacial”, IPL therapy is designed to treat a range of skin conditions including sun damage, age spots and unwanted hair.
While an LED laser uses a single focussed wavelength, the light used in IPL is designed to reach a larger surface area. IPL is also more intense than LED, so while highly effective, it also carries more risk of side effects like discomfort and redness, although this usually fades within a few days.
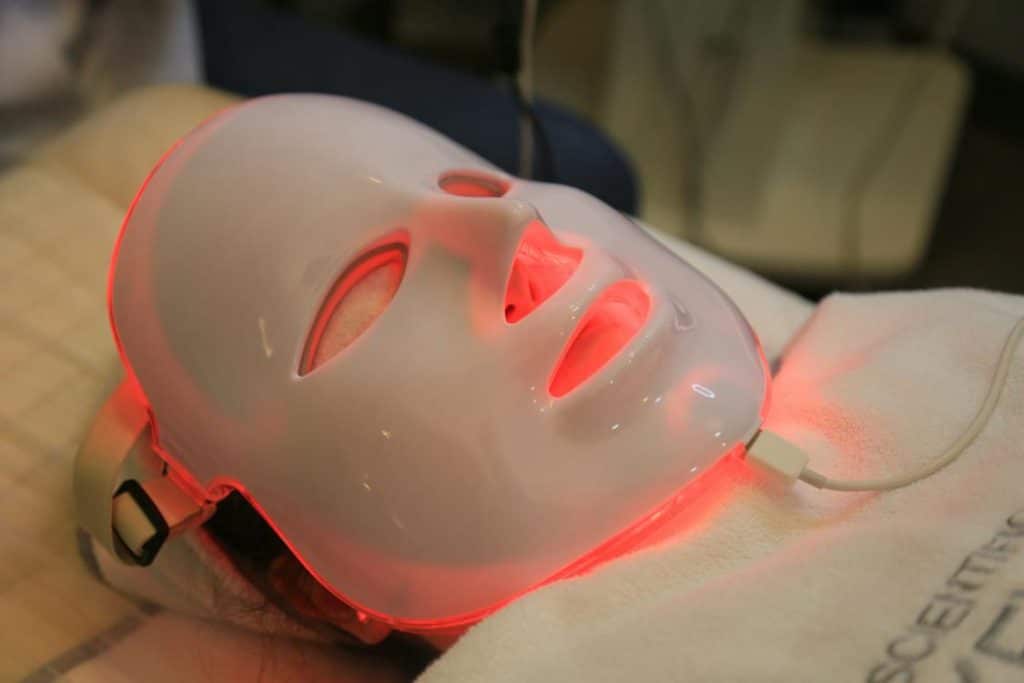
Light Emitting Diodes (LED)
Non-ablative LED treatments (i.e. those which do not remove the top layer of skin) are considered gentler than IPL, making them a better option for those with sensitive or compromised skin. Some forms of LED light therapy include:
- Blue: Used for treatment of acne, eczema and psoriasis.
- Red: Reduces redness and pore size while increasing circulation, hydration and regulating sebum levels.
- Near Infra-Red: Reduces pain, inflammation and promotes healing. Also helps to promote cell absorption and skin elasticity.
How Does Light Therapy Work, and Is It Safe?
Unlike UV rays, which are well-known to cause skin damage and in some cases even cancer, treatments such as LED light therapy use non-ionizing radiation, which is unable to damage DNA or cellular structure in the same way.
In both IPL and LED therapy, light stimulates the cells, boosting collagen production, improving circulation and cellular regeneration. This in turn improves the overall appearance of the skin, making it appear smoother and clearer.
Safety
While light therapies are considered safe for short term use, it’s important to protect your eyes – especially for those with underlying eye conditions or people who are taking medicines which can increase light sensitivity in the eyes.
Before attempting any form of phototherapy, whether at home or by a professional, consult a doctor to assess whether it is safe. It may not be recommended for people who are pregnant, prone to seizures, taking certain medications or have pre-existing skin conditions which could be made worse.
In-Office or At-Home?
Over the last few years, more skincare products designed to replicate treatments typically found in salons have become readily available for use in the home. It’s important to make sure any products you use are FDA-approved.
While at-home treatments are convenient to use, their efficacy isn’t always guaranteed, and they’re less likely to produce the same results that would be achieved through treatment by a trusted dermatologist or esthetician.
If choosing a professional light therapy treatment, find a licensed professional who will offer a proper pre-treatment consultation, including advice on preparation and aftercare; for example, avoiding any medications or treatments that could cause light sensitivity or blood thinning.


